
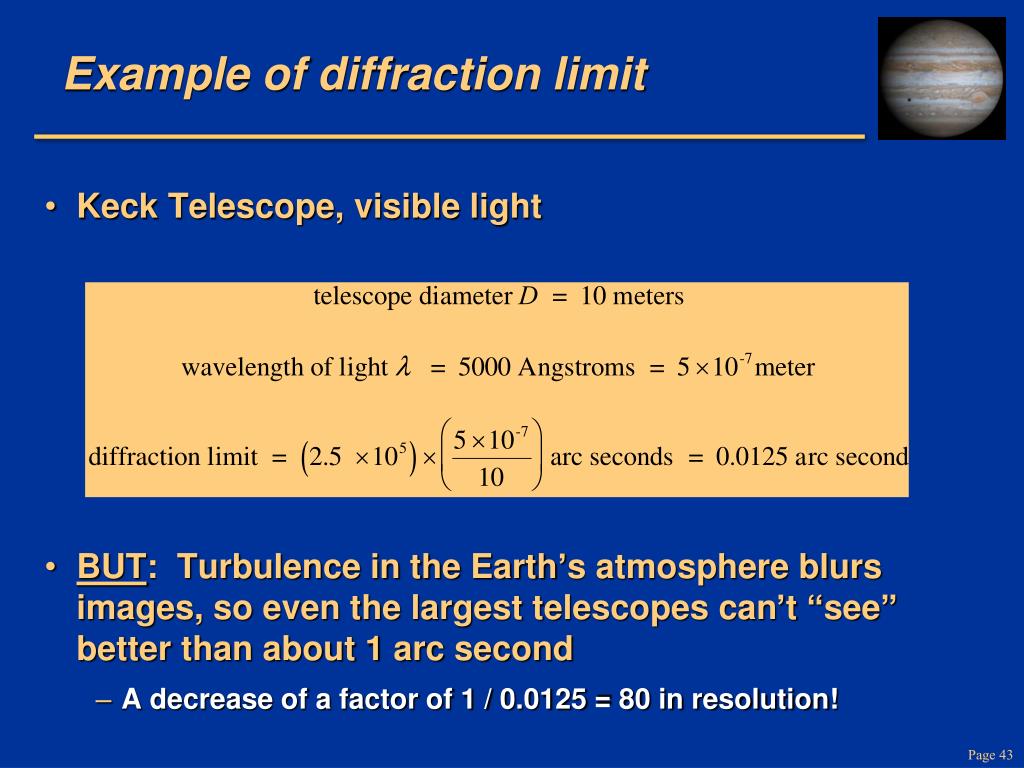
ITu2E.1 Imaging Systems and Applications (ISA) 2013. Circumventing the far-field diffraction limit in optical nanopatterning. This result is consistent with energy principles as follows: If the electric field amplitude at the focus. Meanwhile, the focused spot area, where is the area of the beam. The diffraction limited resolution in angle space is given by alpha 2.44 x wavelength/Diameter, where alpha is in radians. The refractive index n is applied to account for different media, and the resolution limit. AW4N.2 CLEO: Applications and Technology (CLEOAT) 2021. The focused spot size, found from diffraction theory, is approximately where is the diameter of the beam and/or the diameter of the focusing mirror (the smaller of the two). From this, Abbe was able to deduce the resolution limit of a microscope as governed by the equation dSin (). The diffraction-limited angular resolution of a telescopic instrument is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the light being observed, and proportional. The Fraunhofer diffraction equation is an approximation which can be applied when the diffracted wave is observed in the far field, and also when a lens is used to focus the diffracted light in many instances, a simple analytical solution is available to the Fraunhofer equation – several of these are derived below.ĭiffraction geometry, showing aperture (or diffracting object) plane and image plane, with coordinate system. The limiting case may be obtained by setting the diffraction angle equal to the largest angle that can be collected by the objective. The Kirchhoff diffraction equation provides an expression, derived from the wave equation, which describes the wave diffracted by an aperture analytical solutions to this equation are not available for most configurations. What does this have to do with optical systems The concept means that for a finite aperture, there is a fundamental limit to the angular resolution, which is. When a beam of light is partly blocked by an obstacle, some of the light is scattered around the object, and light and dark bands are often seen at the edge of the shadow – this effect is known as diffraction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
